
Date | 2026-02-04 09:51:25
In modern electrical and industrial systems, flame retardancy is often treated as a primary material selection criterion. Safety certifications, regulatory requirements, and fire prevention standards all emphasize resistance to ignition and flame propagation.
However, real-world field failures often reveal a different story.
In many cases, components do not fail because they ignite — they fail because they deform, loosen, or lose dimensional precision long before fire becomes a risk. This raises an important engineering question:
In actual operating environments, which performance parameter becomes the first point of failure — flame retardancy or dimensional stability?
Understanding this relationship is essential when designing high-reliability components for power distribution, motors, rail transit, and new energy systems.
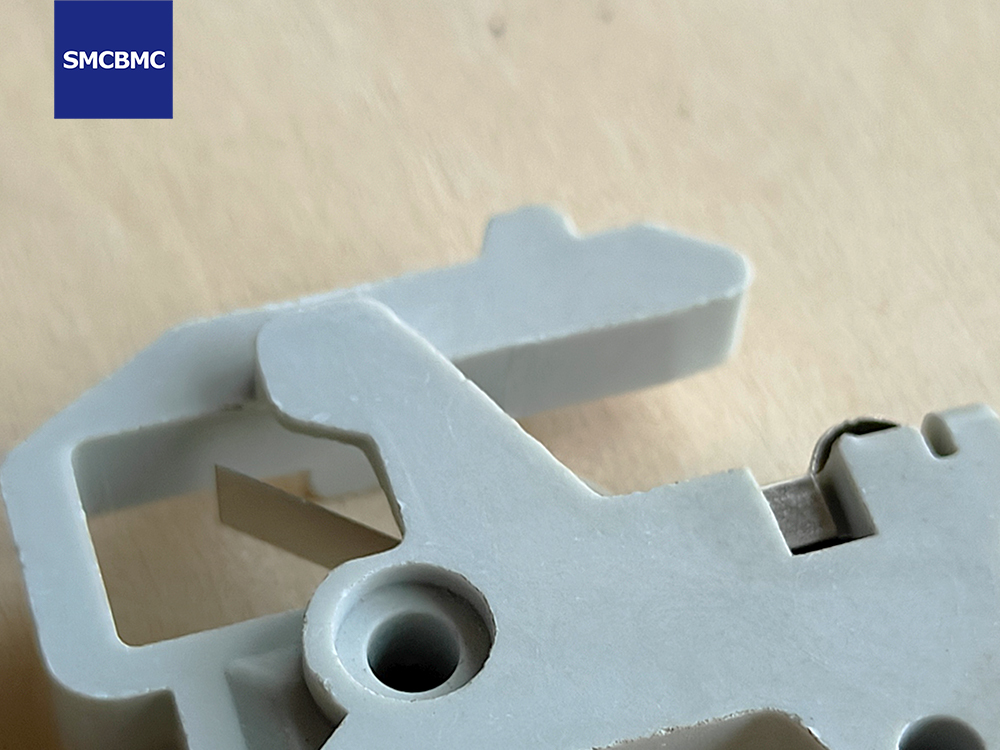
Flame retardancy is critical for electrical safety compliance. Materials used in switchgear, circuit breakers, battery systems, and insulation structures must meet strict regulatory requirements such as UL94 V-0 or equivalent fire performance standards.
Flame retardant materials provide:
Resistance to ignition
Self-extinguishing behavior
Reduced flame propagation
Protection during short-circuit or overload events
For many industries, achieving flame retardancy is considered a baseline requirement rather than a differentiating feature.
However, flame retardancy primarily addresses extreme failure scenarios, not everyday operational stresses.
Electrical and mechanical systems operate continuously under combined environmental and mechanical loads, including:
Thermal cycling
Mechanical preload and vibration
Humidity exposure
Long-term electrical stress
Outdoor weathering and UV exposure
Under these conditions, components may gradually experience:
Loss of mechanical clamping force
Increased contact resistance
Reduced creepage and clearance distances
Seal failure in enclosures
Progressive misalignment of conductive structures
These failures rarely trigger immediate fire hazards but significantly reduce system reliability and lifespan. Over time, dimensional drift can indirectly increase electrical risk, making it a root cause of long-term performance degradation.
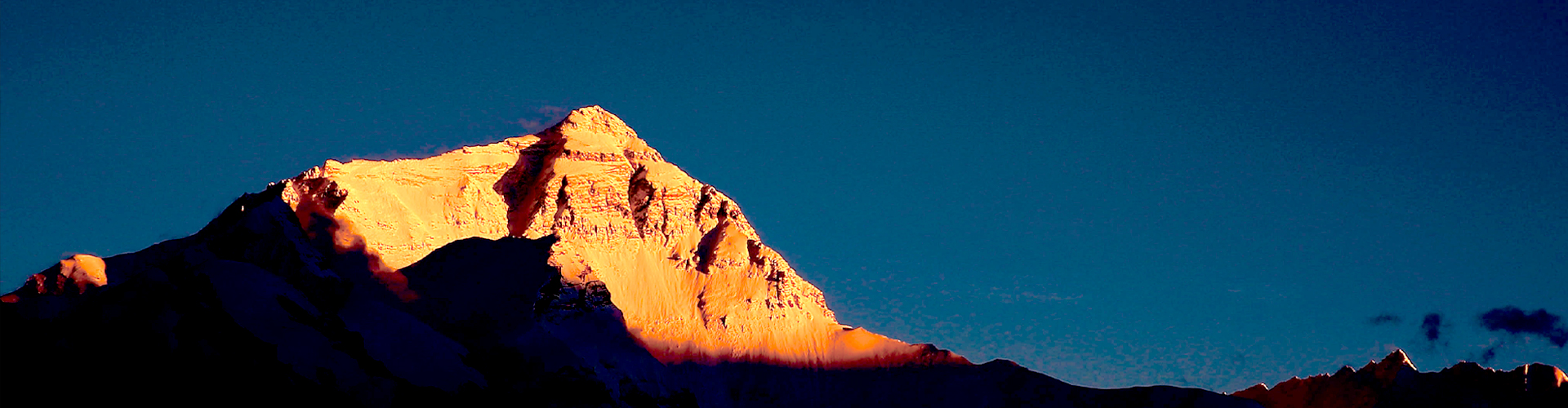
Dimensional stability refers to a material’s ability to maintain its original geometry throughout temperature changes, mechanical loading, and environmental exposure.
In high-voltage and precision electrical assemblies, dimensional integrity directly influences:
Electrical insulation performance
Contact reliability
Structural load distribution
Assembly tolerance control
Long-term sealing effectiveness
Even slight deformation can compromise system safety margins, particularly in compact designs where creepage distances and mechanical tolerances are tightly controlled.
Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) offers a unique combination of flame retardancy and dimensional reliability because of its thermosetting composite structure.
Unlike thermoplastics, BMC forms a permanently crosslinked structure during curing. This prevents material softening or flow when exposed to elevated temperatures, maintaining dimensional accuracy over time.
Glass fiber reinforcement and mineral fillers provide:
Reduced thermal expansion
Improved creep resistance under sustained load
Enhanced structural rigidity
Consistent shrinkage behavior during molding
BMC demonstrates extremely low water absorption compared to hygroscopic engineering plastics, preventing swelling and dimensional distortion in humid environments.
Modern BMC formulations can achieve high flame retardancy levels, including UL94 V-0 classification, without significantly compromising mechanical or dimensional performance.
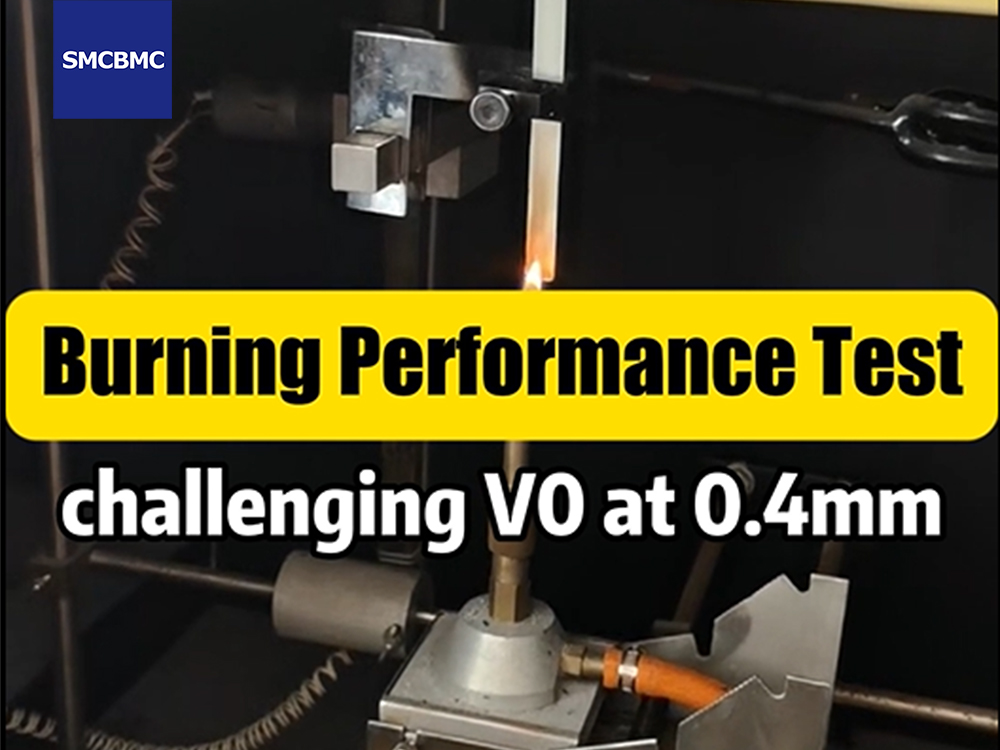
Many flame-retardant thermoplastics meet fire safety standards but remain vulnerable to:
Thermal deformation
Long-term creep
Stress relaxation under mechanical loading
Moisture-induced dimensional changes
In such cases, components may pass safety certification but fail during long-term service due to loss of structural integrity.
BMC helps bridge this gap by providing simultaneous control over fire performance and dimensional reliability.
Dimensional stability cannot be achieved through material formulation alone. It requires precise coordination between:
Material composition
Mold design
Processing parameters
At Wenzhou Jintong, dimensional reliability is engineered through:
Application-specific BMC material development
Mold designs optimized for fiber orientation and shrinkage balance
Uniform mold temperature control
Optimized compression pressure and curing cycles
Batch-level process consistency monitoring
This integrated manufacturing approach ensures that laboratory performance translates into repeatable industrial production quality.
For engineers and OEM manufacturers, the most critical question is no longer:
“Is the material flame retardant?”
But rather:
“Will the material maintain structural and electrical integrity throughout its service life?”
In many applications, flame resistance protects against catastrophic events, while dimensional stability determines everyday operational reliability.
True system safety requires both.
As electrical systems become more compact, energy-dense, and performance-sensitive, material selection must consider long-term structural consistency alongside traditional safety metrics.
BMC is not simply a flame-retardant composite — it is a reliability-focused engineering material designed to maintain dimensional integrity across demanding operational environments.

Wenzhou Jintong Complete Electrical Co., Ltd. specializes in high-performance BMC/SMC thermosetting composites, precision mold design, and compression molding of critical electrical and structural components.
We provide integrated solutions for electrical insulation systems, motors, rail transit equipment, new energy infrastructure, and industrial applications, delivering materials and components engineered for safety, stability, and long-term reliability.