
Date | 2026-01-17 08:12:32
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are critical safety components in residential, commercial, and industrial power distribution systems. While much attention is given to electrical design, the housing material of an MCB is equally decisive for safety, reliability, and long-term performance.
In recent years, thermoplastics have been widely used due to low initial cost and easy processing. However, leading manufacturers are increasingly shifting back to thermosetting composites, especially BMC (Bulk Molding Compound), as safety requirements, short-circuit risks, and fire regulations become more stringent.
This article explains why thermosetting composites are inherently safer than thermoplastics for MCB housings, from a materials science and real-world operating perspective.
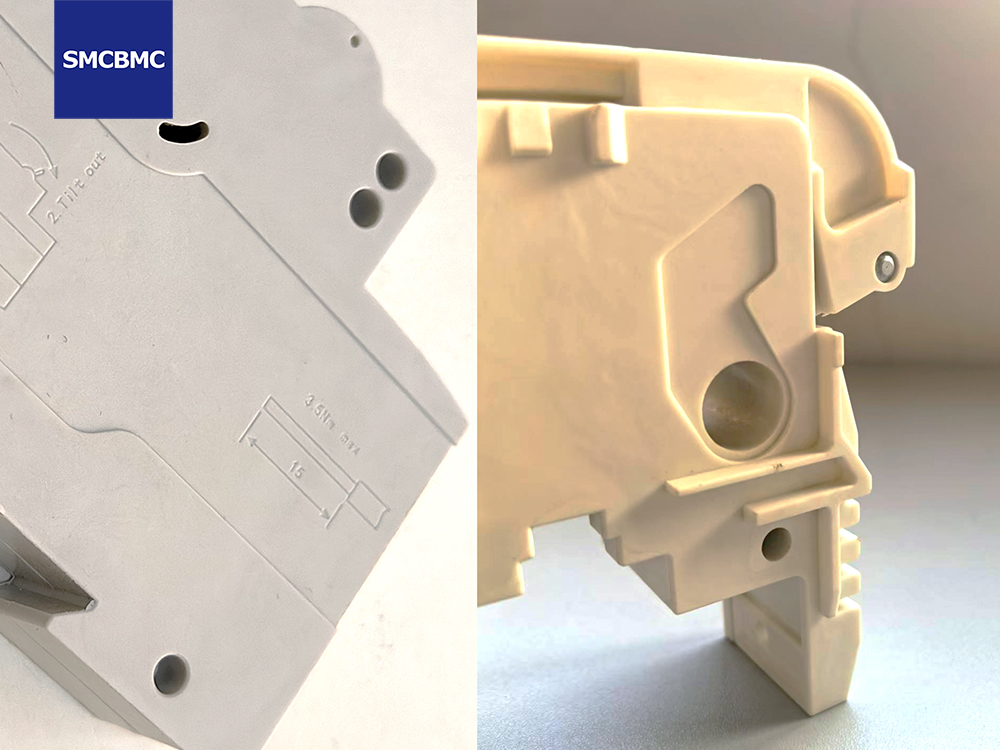
Thermoplastics soften when exposed to high temperatures. During short-circuit events or internal arcing, temperatures inside an MCB can rise sharply within milliseconds. In such conditions, thermoplastics may:
Soften or deform
Melt and drip, spreading fire
Lose structural integrity
Expose live conductive parts
Even flame-retardant thermoplastics rely heavily on chemical additives, whose effectiveness may degrade over time.
Thermosetting composites like BMC undergo irreversible crosslinking during curing. Once formed, they do not melt or flow again, even under extreme heat.
Key advantages include:
No melting or dripping
Self-extinguishing behavior
Stable structure during fault conditions
Flame retardancy up to UL94 V-0 without halogen additives
This fundamental difference alone makes thermosetting materials far safer for MCB housings.
During a short circuit, an MCB housing must withstand:
Extremely high temperatures
Electrical arcs
Sudden mechanical shock
Rapid pressure changes
BMC-based housings excel in these conditions due to:
High arc resistance
Excellent tracking resistance (high CTI values)
Low smoke generation
Strong resistance to carbonization
Unlike thermoplastics, which may carbonize and create conductive paths, thermosetting composites maintain electrical insulation even after arc exposure.
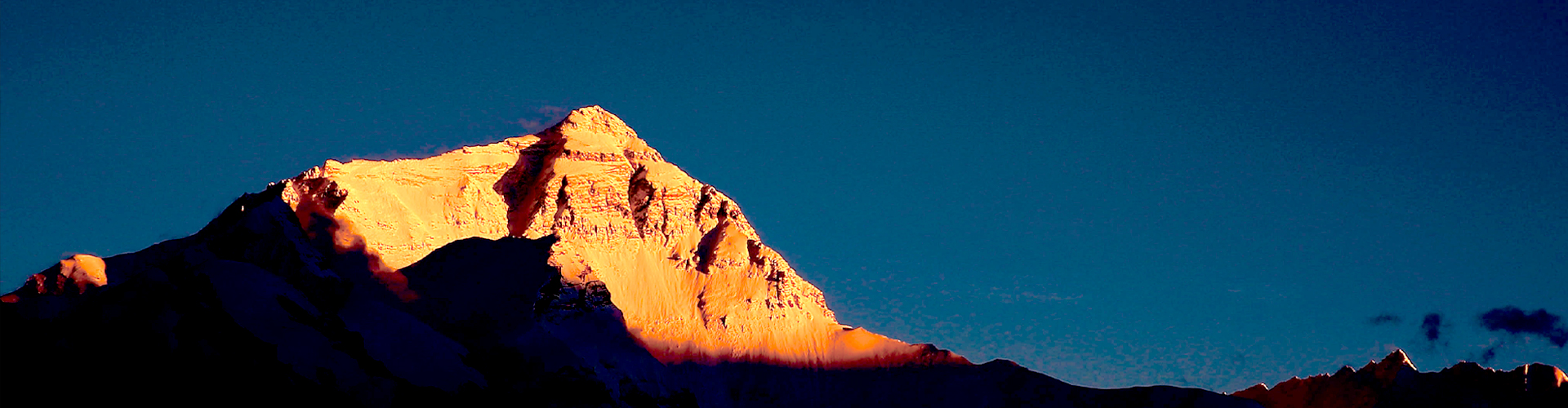
MCBs require precise tolerances to ensure correct tripping behavior and mechanical operation.
Thermoplastics typically exhibit:
Higher thermal expansion
Creep under long-term stress
Deformation at elevated temperatures
Thermosetting composites offer:
Low thermal expansion
Excellent creep resistance
Stable dimensions over decades of operation
This ensures consistent performance over the entire service life of the circuit breaker, even in hot panels or densely packed distribution boards.
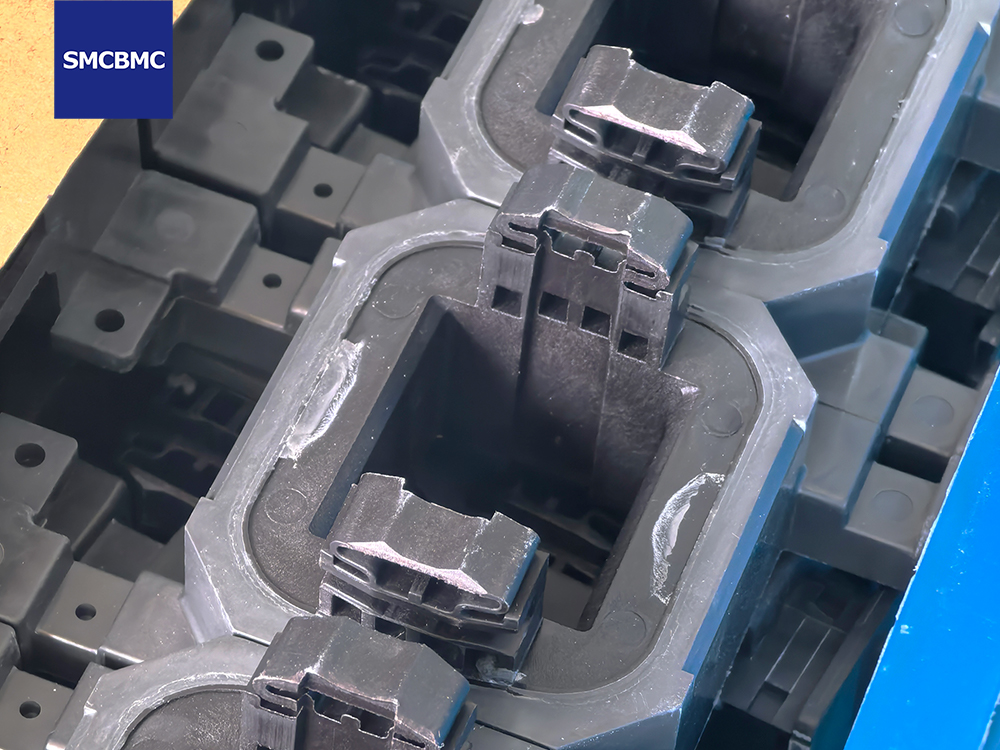
MCB housings must survive:
Assembly stress
Screw torque
Repeated switching
Vibration during transport and installation
BMC materials combine high mechanical strength with rigidity, reinforced by glass fibers. Compared to thermoplastics, they show:
Higher flexural strength
Better impact resistance at elevated temperatures
No softening under load
This makes thermosetting composites especially suitable for industrial-grade and high-reliability MCBs.
As electrical safety regulations tighten worldwide, thermosetting composites provide a safer compliance path:
UL94 V-0 flame rating
High CTI values for pollution degree environments
Better compliance with IEC standards
Reduced risk of recall due to material failure
For manufacturers targeting global markets, BMC housings significantly reduce certification and long-term liability risks.
Choosing the right material for an MCB housing is not a cost decision—it is a safety decision.
While thermoplastics may appear economical upfront, thermosetting composites deliver superior fire safety, arc resistance, dimensional stability, and long-term reliability. That is why they remain the preferred choice for high-performance and safety-critical circuit breakers.
In modern power distribution systems, thermosetting composites are not an alternative—they are the benchmark.

Jintong specializes in BMC and SMC thermosetting composite materials, precision molds, and compression-molded components for electrical applications.
We support global MCB manufacturers with:
Customized BMC formulations
Precision mold development
Stable mass production
Full compliance with IEC and UL requirements
From material science to reliable products, we help you build safer electrical systems.